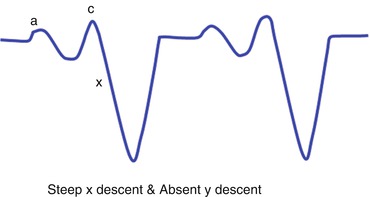
Y Descent Tamponade
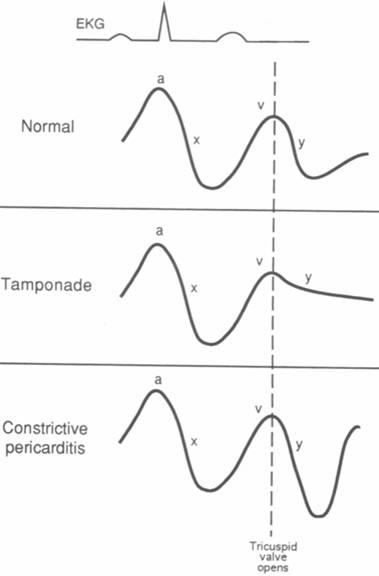
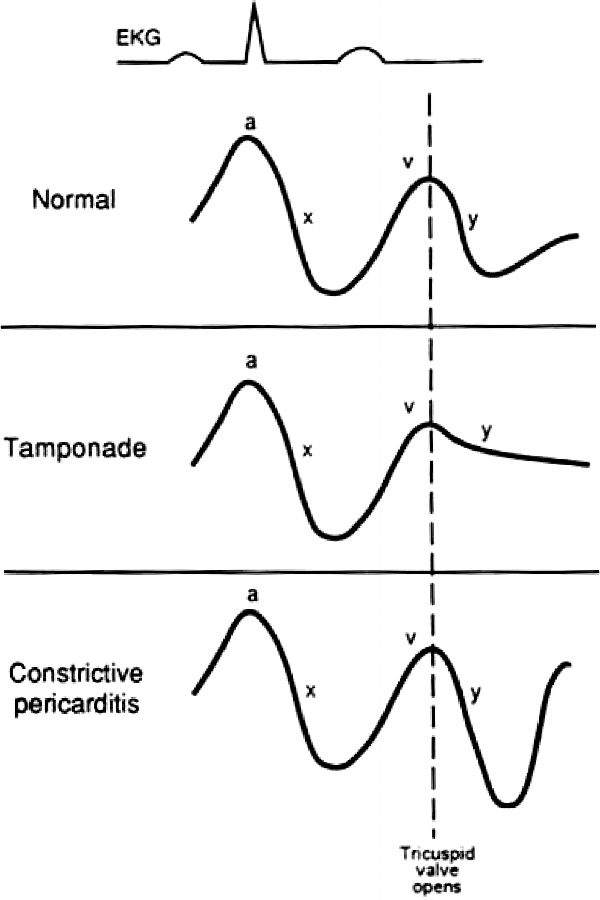
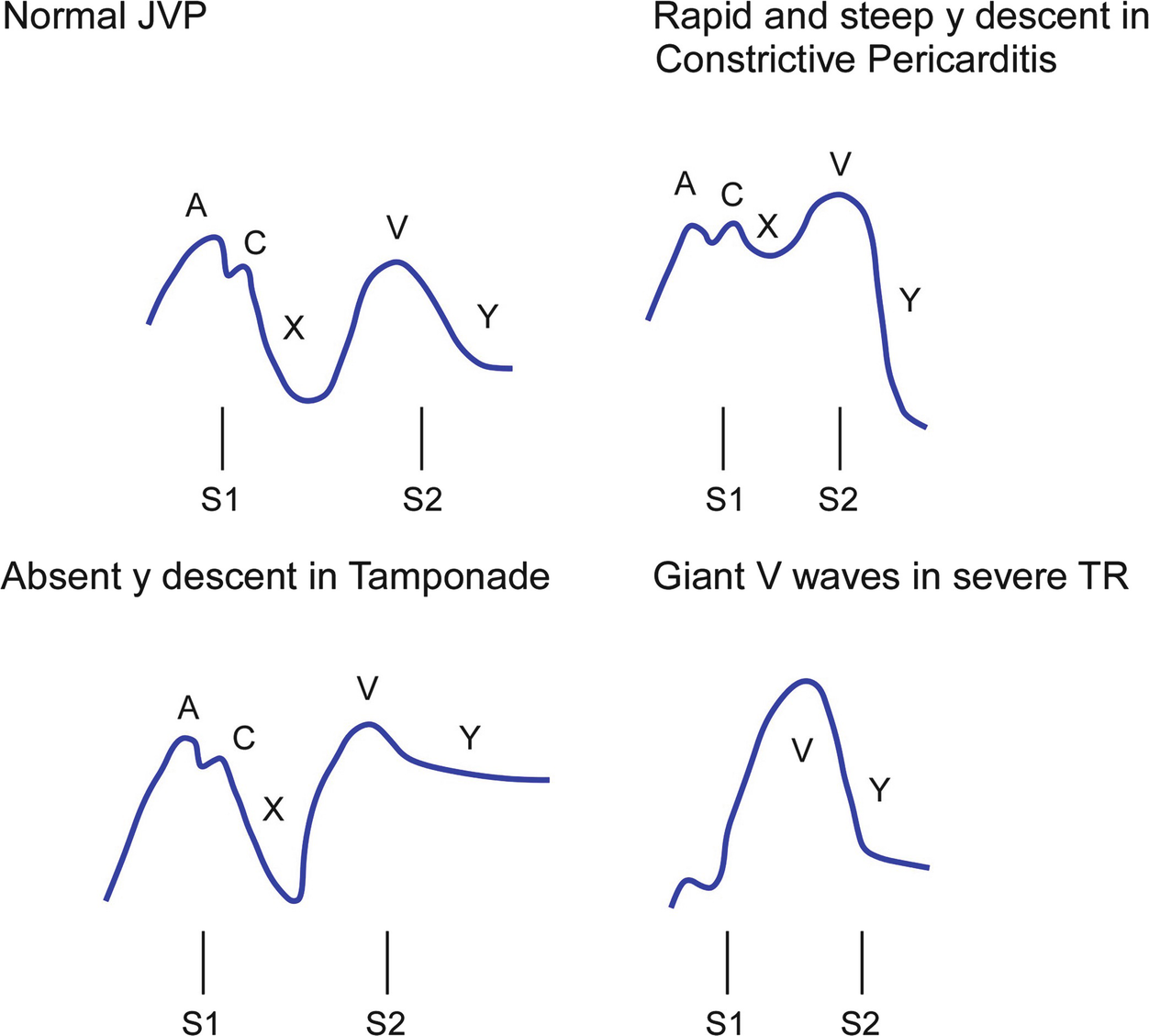
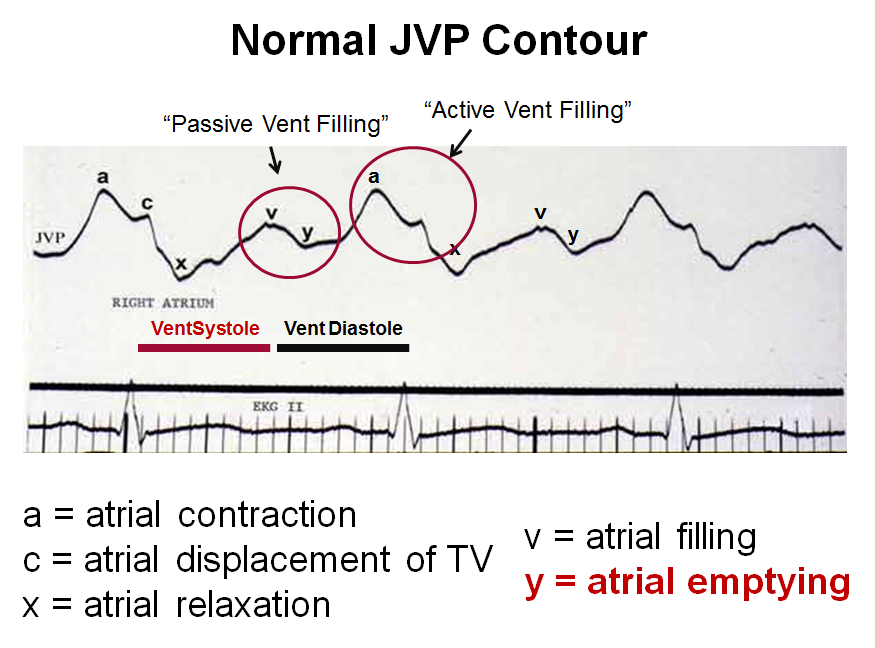
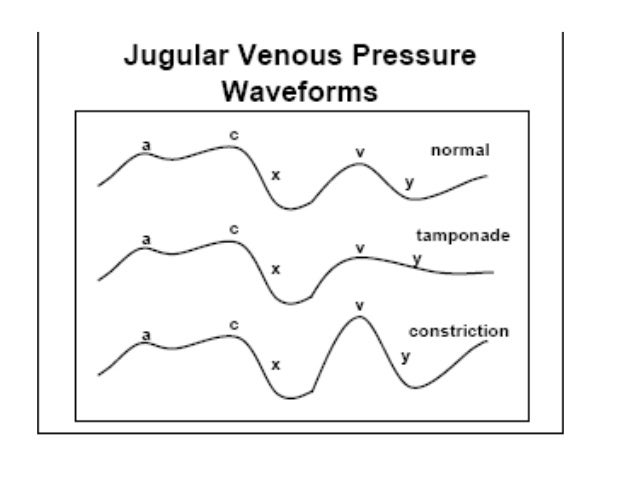
The y descent corresponds to the rapid emptying of the atrium into the ventricle following the opening of the tricuspid valve.
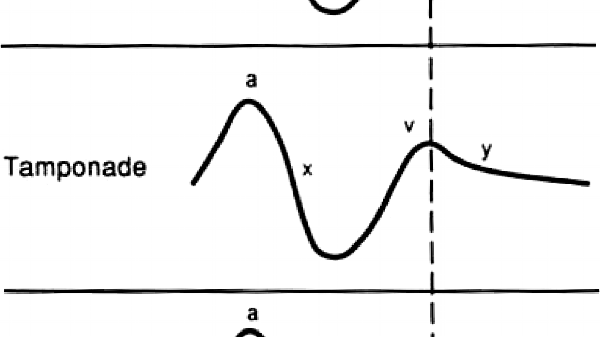
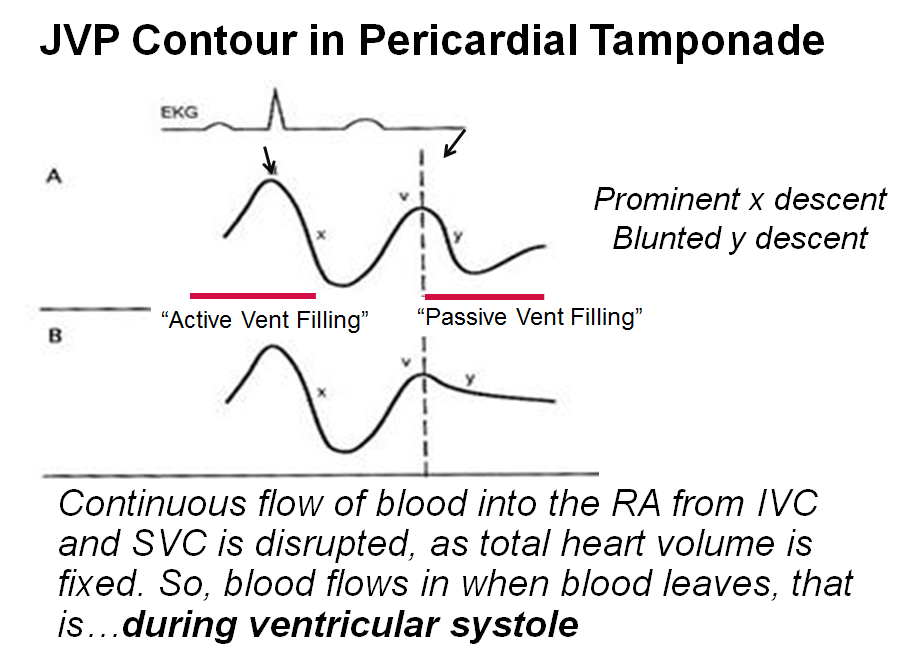
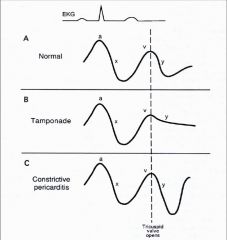
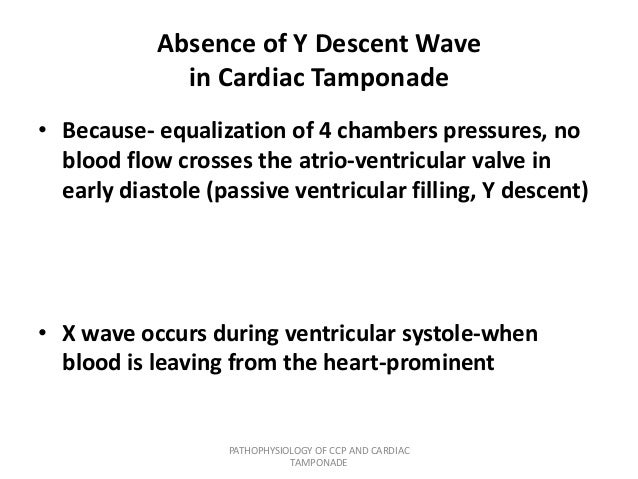
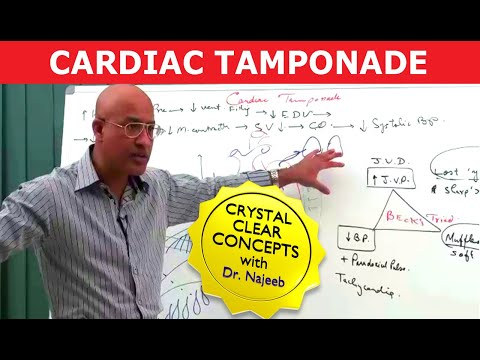
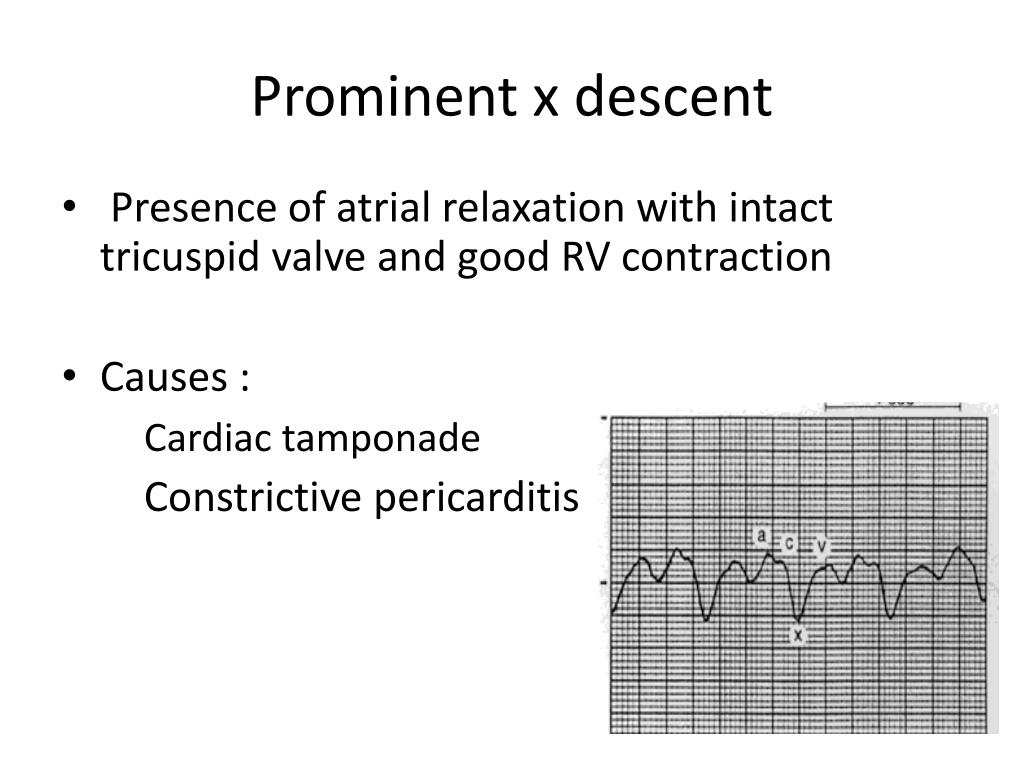
Y descent tamponade. Lost of y descent when the tricuspid valve opens pressure goes down atria start emptying and ventricles start filling leads to produce y descent. Take home points cardiac tamponade is a clinical diagnosis. Unlike cp a pronounced x descent is not seen figure 1. It has since been modified in various ways.
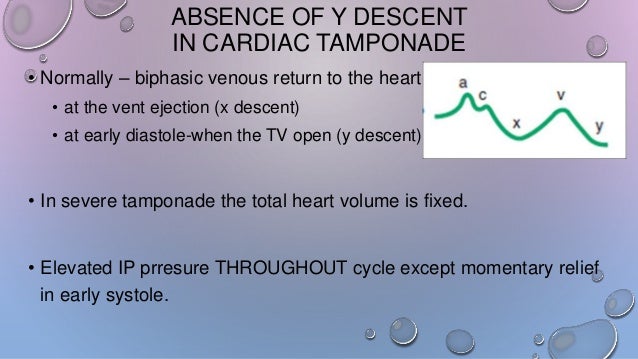
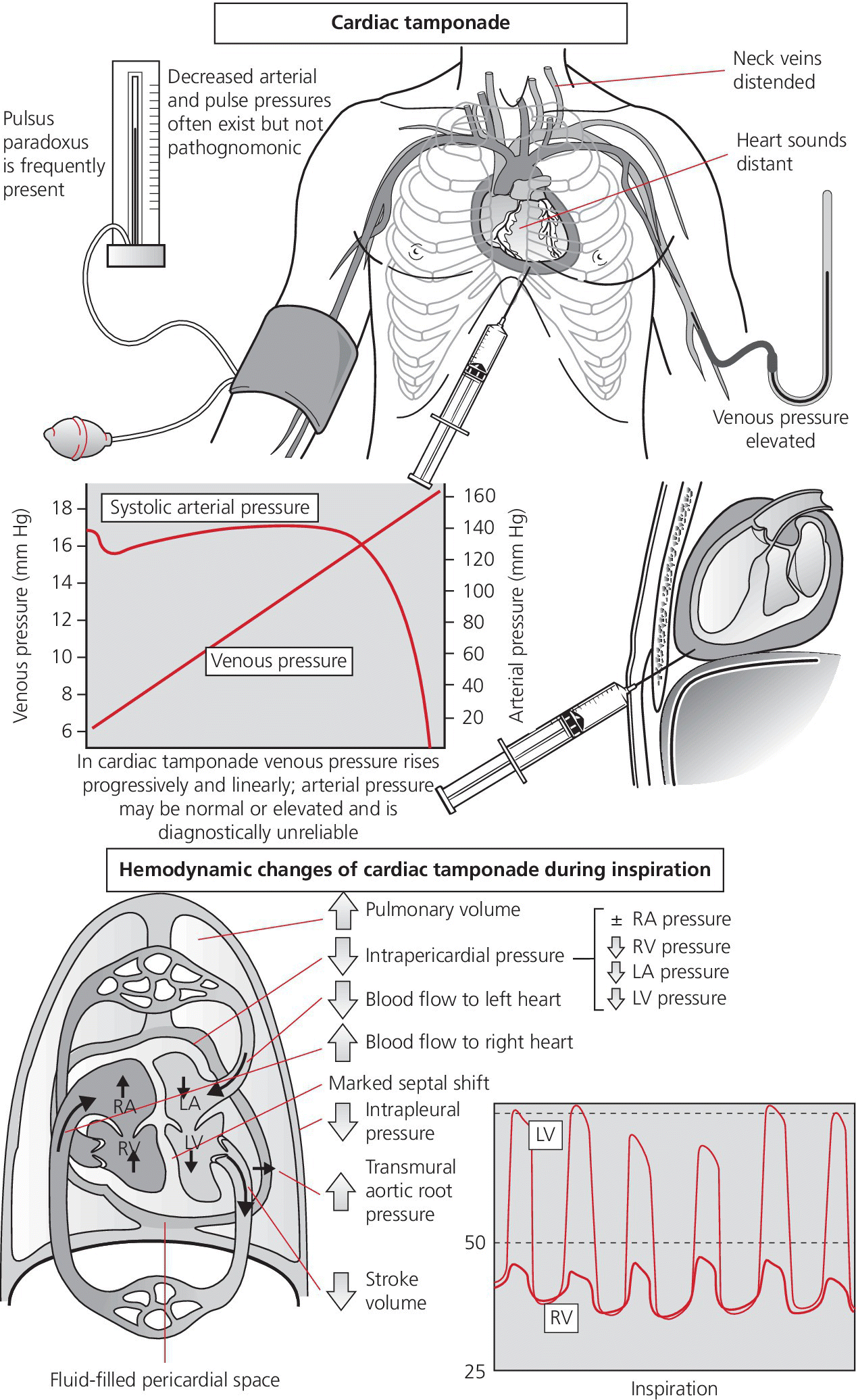
This is due to an increase in intrapericardial pressure preventing diastolic filling of the ventricles. In cardiac tamponade as cardiac chamber is strangulated even after the opening of tricuspid valve blood cannot rapidly fall down due to high pressure in ventricles so y descent is lost. Kussmaul s sign may be present in rcm and is therefore a nonspecific finding 32 33 aprominent y descent is seen on the jugular venous contour accompanied by an s3 given rapid early filling of a stiffened ventricle. In pericardial tamponade x descent is seen.
Posted by ikan nakeya dewaswala bhopalwala m d. The presence of a rapid y descent excludes the diagnosis of pericardial tamponade. Electrocardiogram and laboratory testing. The y descent is abolished in the jugular venous or right atrial waveform.
Realistically these changes are often lost in the noise. In cardiac tamponade the y descent is blunted b c of the fluid in the pericardium that stops the ventricles from expanding so why isn t this the case with constrictive pericarditis since the pericardium is stiff. Thank you so much for sending your mnemonics to us girl. Jvp doesn t change with respiration kussmaul sign.
A prominent y descent has been found to occur in about one third of the patients with constrictive pericarditis and two thirds of patients with right ventricular infarction. In pericarditis y descent is seen. Diagnosis tamponade elevated diastolic pressures equal end diastolic pressures in rv or lv or pcwp absence of ventricular filling early in diastole absence of y descent in atrial tracings diagnosis constrictive pericarditis elevated diastolic pressures equalization of diastolic pressures in the rv and lv completion of diastolic filling in early diastole dip and plateau in ventricular trace rapid x and y descents kussmal s clinical occurrence penetrating trauma aortic. A venous arch may be used to measure the jvp more accurately.